Small Business Frequently Asked Questions – Top 5 FAQ
Starting and running a small business comes with a complex set of questions, many of which revolve around finance, staffing, and technology. Getting these fundamentals right is crucial for compliance, profitability, and efficiency as well. Below are five of the small business frequently asked questions we hear, with our clear and concise answers, so let’s jump right in…
1. How Many Pay Periods Are in a Year?
The number of pay periods in a year depends entirely on the pay schedule and frequency your business chooses. There are four common payroll schedules:
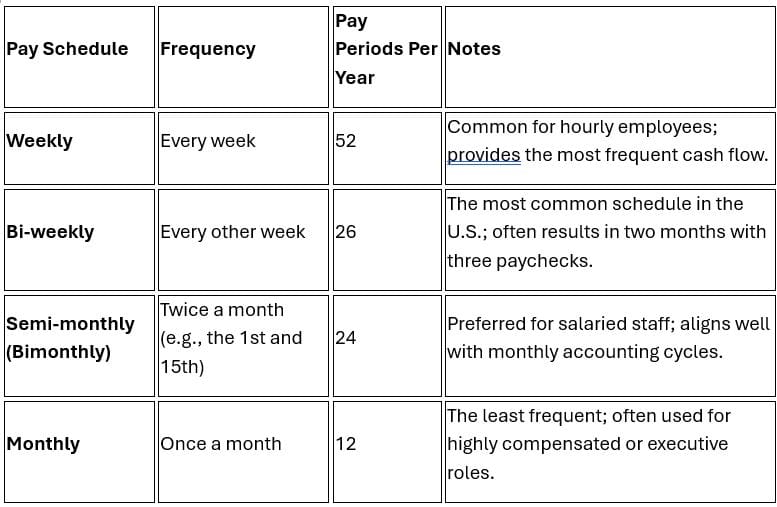
For small businesses with hourly employees, bi-weekly or weekly schedules are often easiest, particularly for tracking overtime.
For salaried employees, semi-monthly is standard as it simplifies budgeting and tax deductions.
Note that a bi-weekly schedule may occasionally result in 27 pay periods in a calendar year, which requires planning to manage the extra payroll costs.
BizRealtyLab Pro Tip: To review different payroll calendars and better plan your financial year, see this detailed pay period guide from QuickBooks.
2. Should I Pay Employees Hourly Versus Salary?
Although this is #2 on our list, it’s probably tops of the small business frequently asked questions we hear. The choice between hourly versus salary depends on the employee’s role, their eligibility for overtime, and the nature of their work. The table below helps explain.
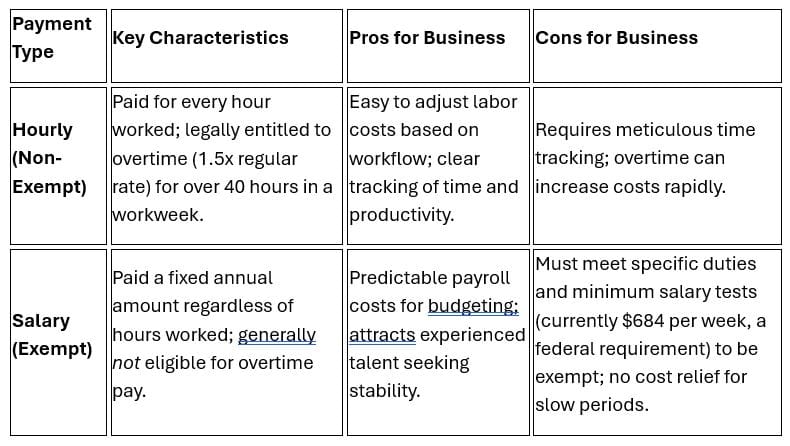
The crucial distinction is ‘exempt’ versus ‘non-exempt’ under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). A position must meet a specific salary threshold and pass a “duties test” (e.g., executive, administrative, professional) to be classified as salary-exempt.
If a worker doesn’t qualify as exempt, you must pay them on an hourly basis, even if you structure their pay as a fixed amount (a non-exempt salaried employee).
3. What is the Difference Between Accrual Basis vs Cash Basis Accounting?
The difference between accrual basis vs cash basis lies in the timing — meaning when revenue and expenses are recorded in your books. This choice dramatically impacts your reported profitability and tax liability.
1. CASH BASIS ACCOUNTING: Transactions are recorded only when cash actually changes hands.
2. ACCRUAL BASIS ACCOUNTING: Transactions are recorded when they are earned or incurred, regardless of when the cash is exchanged.
Most small businesses start on the cash basis due to its simplicity, but the accrual basis is required by Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and the IRS for larger businesses (specifically those with average annual gross receipts over a set threshold or those carrying inventory).
BizRealtyLab Pro Tip: For a side-by-side comparison and detailed examples of accrual basis vs cash basis accounting, click here for Preferred CFO’s Complete Guide.
4. How Do I Perform an EBITDA Calculation?
EBITDA calculation is a vital financial metric, particularly when valuing your business or comparing its operating performance to competitors. EBITDA stands for Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization.
It’s a non-GAAP measure that strips out non-operating expenses (Interest, Taxes) and non-cash expenses (Depreciation, Amortization) to show the profitability generated purely from a company’s core operations.
There are two common ways to calculate EBITDA, starting from figures found on your company’s Income Statement:
1. STARTING FROM NET INCOME (The Bottom Line):
EBITDA = {Net Income} + {Interest Expense} + {Taxes} + {Depreciation} + {Amortization}
2. STARTING FROM OPERATING INCOME (EBIT):
EBITDA = {Operating Income} + {Depreciation} + {Amortization}
Why it matters: Depreciation and amortization are non-cash accounting entries, and interest/taxes relate to financing and governmental policy, not core business efficiency.
By removing them, EBITDA helps you and potential buyers assess the underlying operational profitability.
5. What is the Average Laptop Lifespan for a Small Business?
For a small business, the average laptop lifespan is generally considered to be 3 to 5 years.
While a machine can physically last longer with good maintenance (up to 7 or 8 years, sometimes even longer), the three to five-year window is the industry standard for replacement because of three key factors:
1. Software Obsolescence
After about five years, new operating system versions and essential business software (like video conferencing or robust CRM tools) often require more processing power or memory than older hardware efficiently provides.
2. Security Risks
Depending on the timing of when you bought the machine, older operating systems and hardware may stop receiving critical security updates from the manufacturer, leaving your business vulnerable to cyber threats.
3. Productivity Drain
Slower boot times, sluggish multi-tasking, and frequent crashes severely impact employee productivity, typically making the cost of replacement a worthwhile investment in efficiency alone.
Many businesses follow a 3-year replacement cycle for high-use laptops to ensure peak performance and maintain vendor warranties.
I hope you enjoyed our answers to the top 5 small business frequently asked questions. If you’d like other questions answered, just let us know in the comments or contact us directly anytime.





